Broadly speaking, the FF model intramolecular potential
![]() is a function of a set
is a function of a set
![]() of generalized (nuclear) internal coordinates (IC) describing target molecule
of generalized (nuclear) internal coordinates (IC) describing target molecule ![]() .
Within the JOYCE procedure, the selection of this set is either automatically performed by the program or defined by the user, once the model (i.e. the definition of all interaction sites) mimicking the target molecule has been chosen.
It is worth noticing that the selected IC are not necessarily required to be linearly independent, but redundant (
.
Within the JOYCE procedure, the selection of this set is either automatically performed by the program or defined by the user, once the model (i.e. the definition of all interaction sites) mimicking the target molecule has been chosen.
It is worth noticing that the selected IC are not necessarily required to be linearly independent, but redundant (![]()
![]() 3
3![]() - 6) set of internal coordinates (RIC) can also be employed.
- 6) set of internal coordinates (RIC) can also be employed.
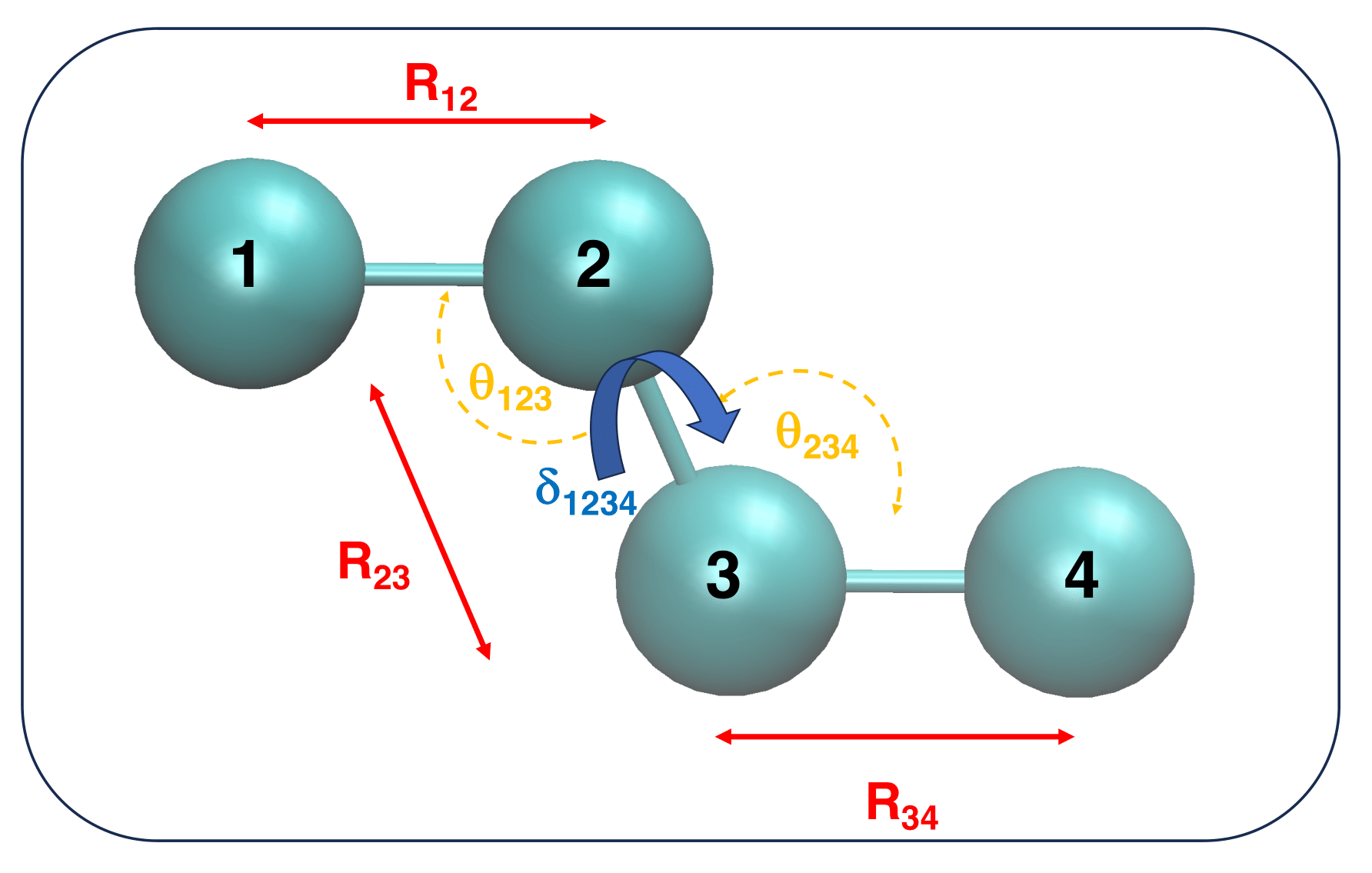
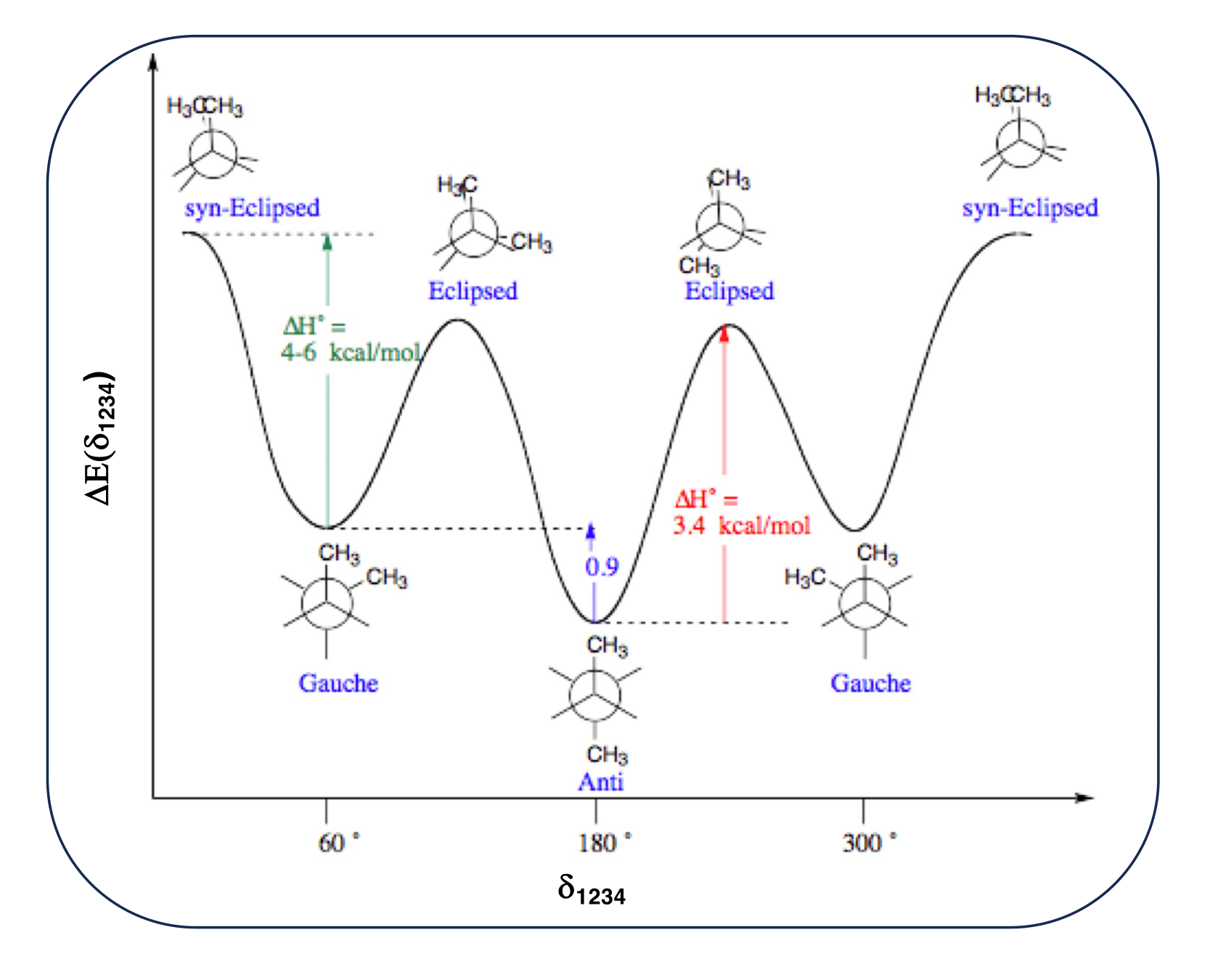
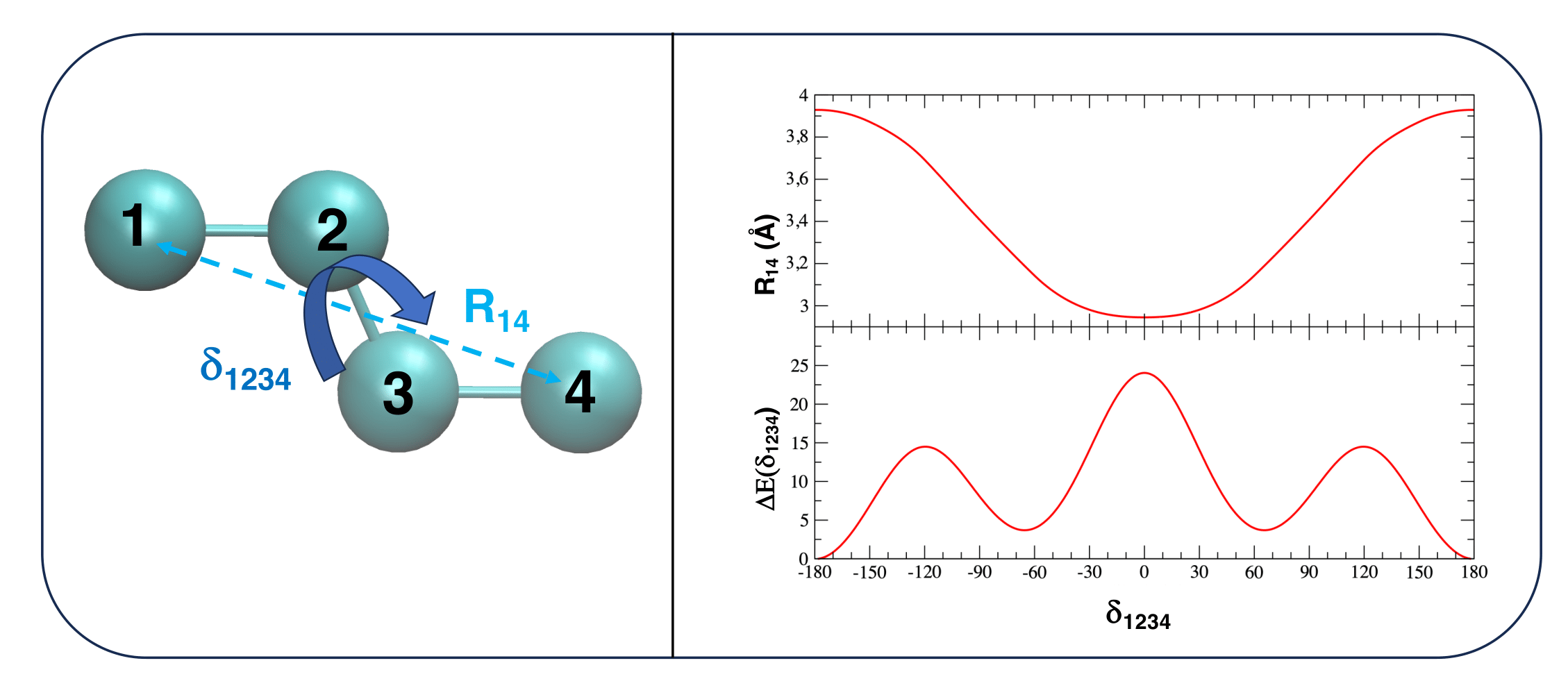
As an example, let's consider the n-butane molecule.
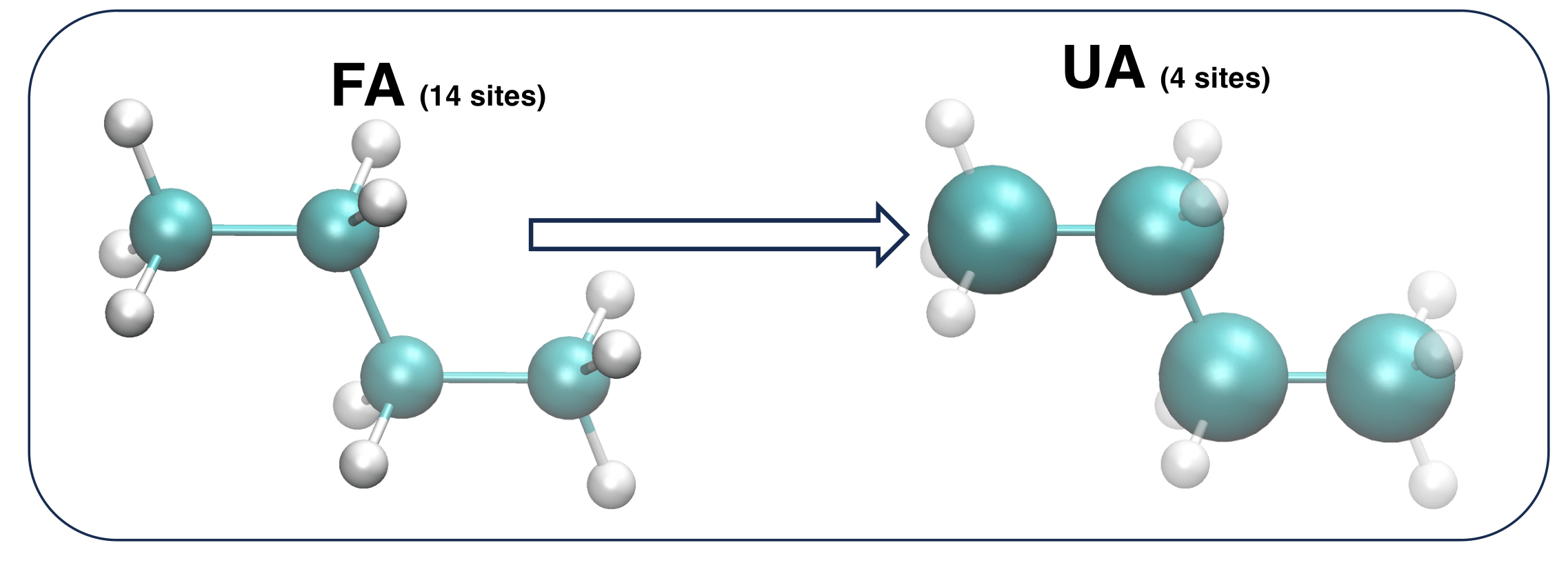
For the sake of clarity, let's also suppose to adopt an united atom (UA) representation, where all Hydrogen atoms are grouped in an unique interaction site with the Carbon atom bonded to them.
Within this model, sketched in Figure 2, the model n-butane molecule is composed by ![]() = 4 interaction sites, whose geometry is completely described by (3
= 4 interaction sites, whose geometry is completely described by (3![]() - 6)=6 IC.
- 6)=6 IC.
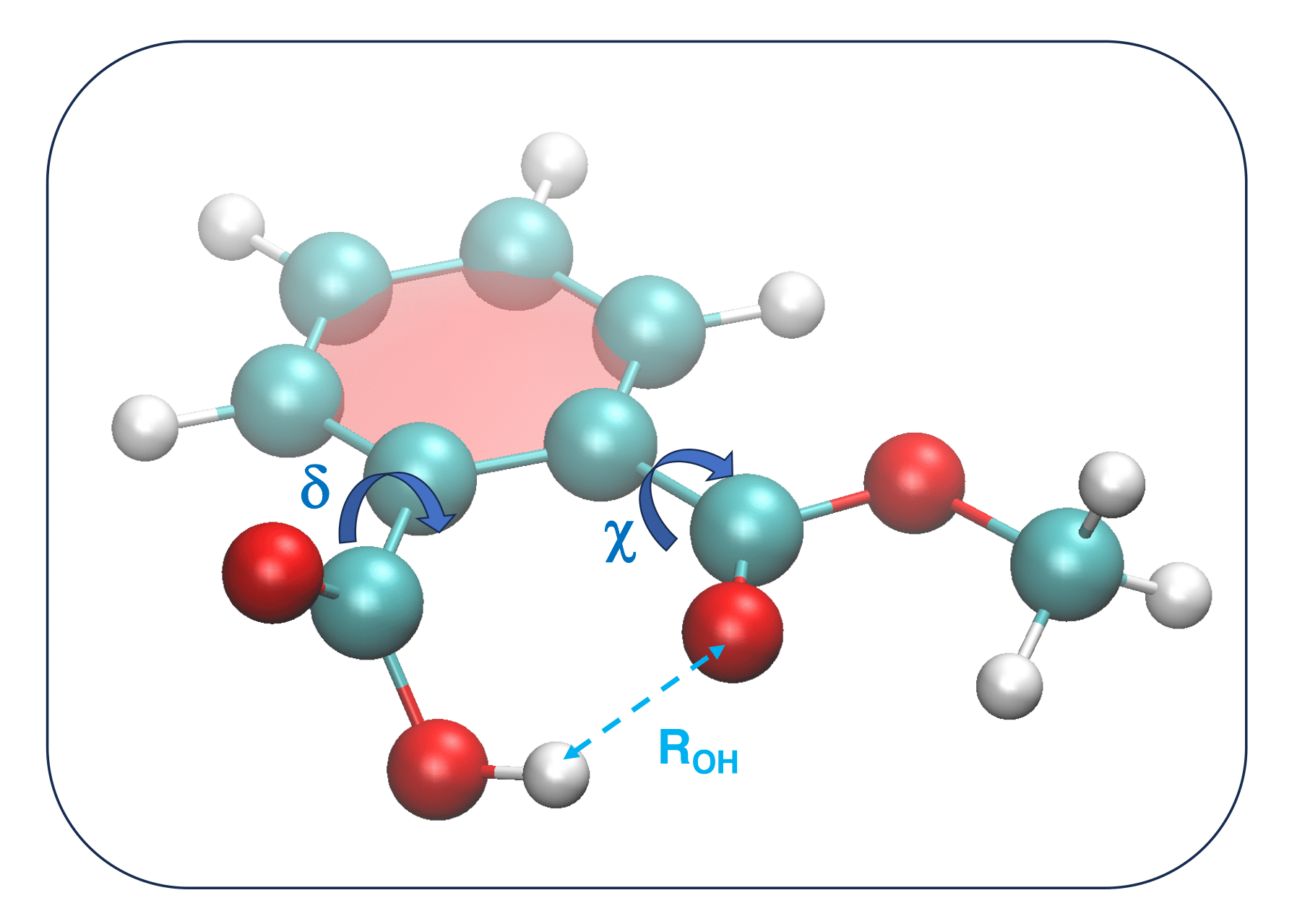
Another type of soft coordinate is the intramolecular distance between a pair of atoms connected by more than two bonds. Despite internal distances are intrinsically redundant (in that they can be expressed as a function of bond lengths, angles and dihedrals defining the relative position of the two atoms defining them), they turn out to be very useful in the case of large molecules, when important interactions between two different molecular regions take place after some geometrical rearrangement. Conversely, their use for smaller molecules does not seem to yield any particular advantage. As an example let's consider two different molecules, namely the PMME-H molecule and n-butane.
A different situation arises for a slightly larger molecule, the PMME-H, shown in Figure 6. One of the lowest energy conformers is characterized by an intramolecular hydrogen bond, evidenced in Figure 6 with a dotted line, between the H atom of the carboxyl group and the Oxygen of the neighboring carboxylate.
As both of these groups can easily change their relative orientation by varying (at least) either ![]() and
and ![]() dihedrals, the internal O-H distance depends on these soft ICs in rather complex fashion.
In such cases, despite not necessary, it is convenient to include intramolecular distances in the RIC set defining the FF.
dihedrals, the internal O-H distance depends on these soft ICs in rather complex fashion.
In such cases, despite not necessary, it is convenient to include intramolecular distances in the RIC set defining the FF.