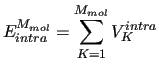The total energy (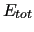 ) of a system of
) of a system of 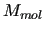 molecules in classical simulation is usually [5,6] computed as a sum of two contributions, namely
molecules in classical simulation is usually [5,6] computed as a sum of two contributions, namely
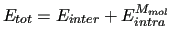 |
|
|
(1) |
where 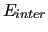 and
and
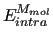 are the interaction energy among different molecules and the sum of the internal energy of each molecule.
In standard FFs,
are the interaction energy among different molecules and the sum of the internal energy of each molecule.
In standard FFs, 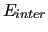 is computed as a sum of pairwise contributions among all the
is computed as a sum of pairwise contributions among all the 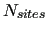 interaction sites used to model the system.
In particular,
interaction sites used to model the system.
In particular,
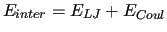 |
|
|
(2) |
where the long-range electrostatic term is
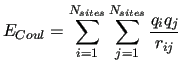 |
|
|
(3) |
whereas the short range 12-6 Lennard-Jones term is
![$\displaystyle E_{LJ} = \sum^{N_{sites}}_{i=1} \sum^{N_{sites}}_{j=1}
4 \epsilon...
...} {r_{ij} } \bigg )^{12} -
\bigg(\frac{ \sigma_{ij} } {r_{ij} } \bigg)^6 \bigg]$](img107.png) |
|
|
(4) |
where 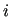 and
and 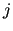 are interaction sites belonging to a pair of different molecules.
are interaction sites belonging to a pair of different molecules.
The total intramolecular term
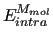 is the sum of the molecular internal energies (
is the sum of the molecular internal energies (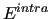 ) of all the
) of all the 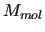 molecules composing the system,
i.e.
molecules composing the system,
i.e.
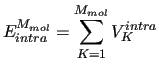 |
|
|
(5) |
where
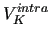 is the internal energy of molecule
is the internal energy of molecule 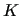 .
.
Given a model potential function
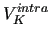 , the main goal of the JOYCE program is to find, with respect of reference QM computed data, the best parameters to represent the intramolecular energy for a chosen target molecule
, the main goal of the JOYCE program is to find, with respect of reference QM computed data, the best parameters to represent the intramolecular energy for a chosen target molecule 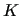 , hence parameterizing the intra-molecular term of a QMD-FF..
, hence parameterizing the intra-molecular term of a QMD-FF..
![]() ) of a system of
) of a system of ![]() molecules in classical simulation is usually [5,6] computed as a sum of two contributions, namely
molecules in classical simulation is usually [5,6] computed as a sum of two contributions, namely
![]() is the sum of the molecular internal energies (
is the sum of the molecular internal energies (![]() ) of all the
) of all the ![]() molecules composing the system,
i.e.
molecules composing the system,
i.e.